SLIDES FOR MULTIMEDIA
3.5
Image copyright
When using images on your slides, make sure that you have the right to use all the images.
- Who owns the copyright of all the photos, graphics or pictures you have used? Are we allowed to use the images?
- If the images are taken from the web, which Creative Commons licence do they have?
If possible, use your own images – you are the copyright owner of those images and are free to use them as you like.
Below are different examples of copyright attributions.
Linking to a journal, with permission from the author:
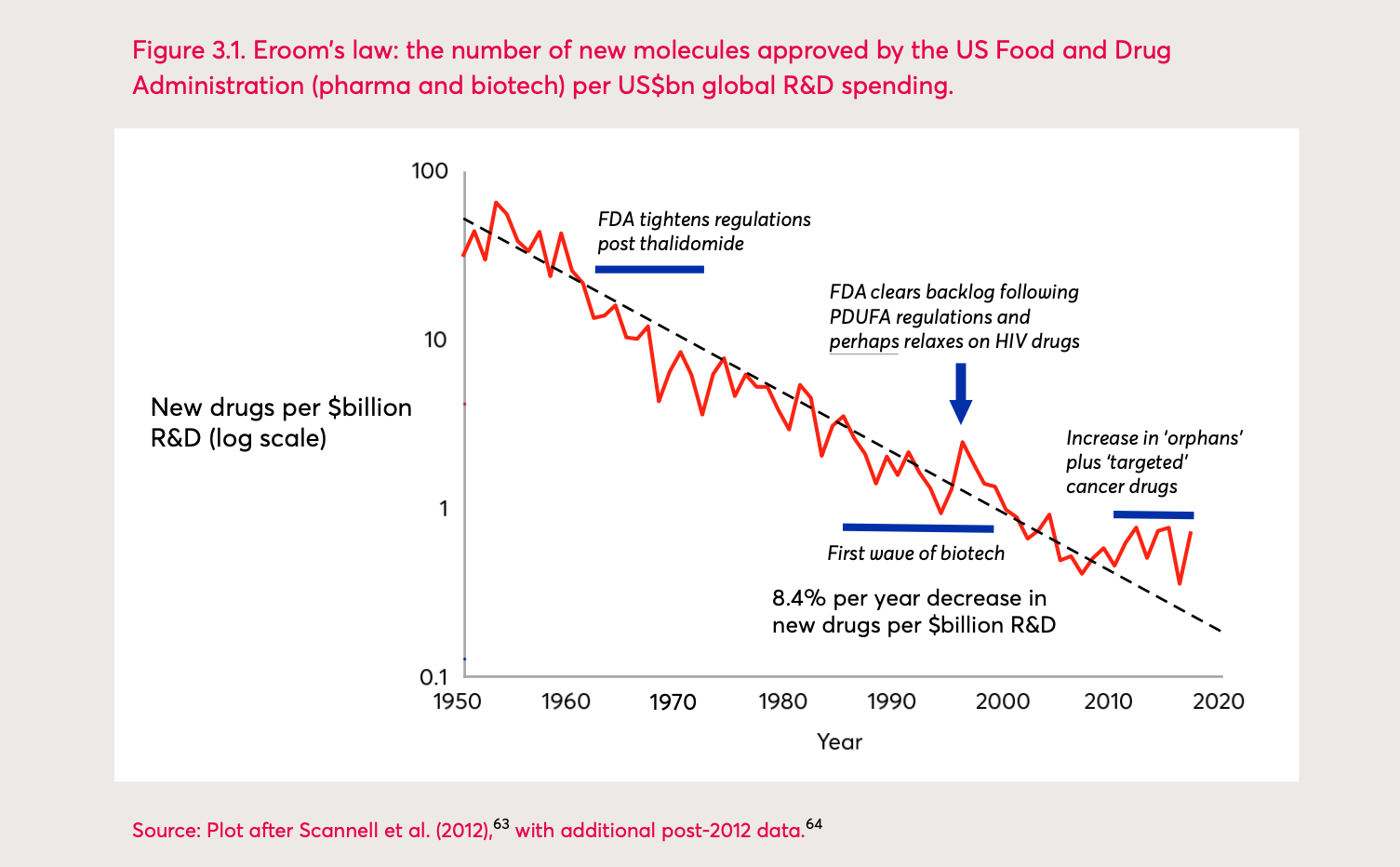
Eroom’s Law: the number of new molecules approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (pharma and biotech) per billion US dollars global R&D spending. Jones R, Wilsdon J. The Biomedical Bubble: Why UK research and innovation needs a greater diversity of priorities, politics, places and people. Report [Internet]. Nesta, London. 2018. Reprinted with permission from James Wilsdon.
From the Massive Open Online Course «Examining African Contributions to Global Health»
Linking to Wikimedia:
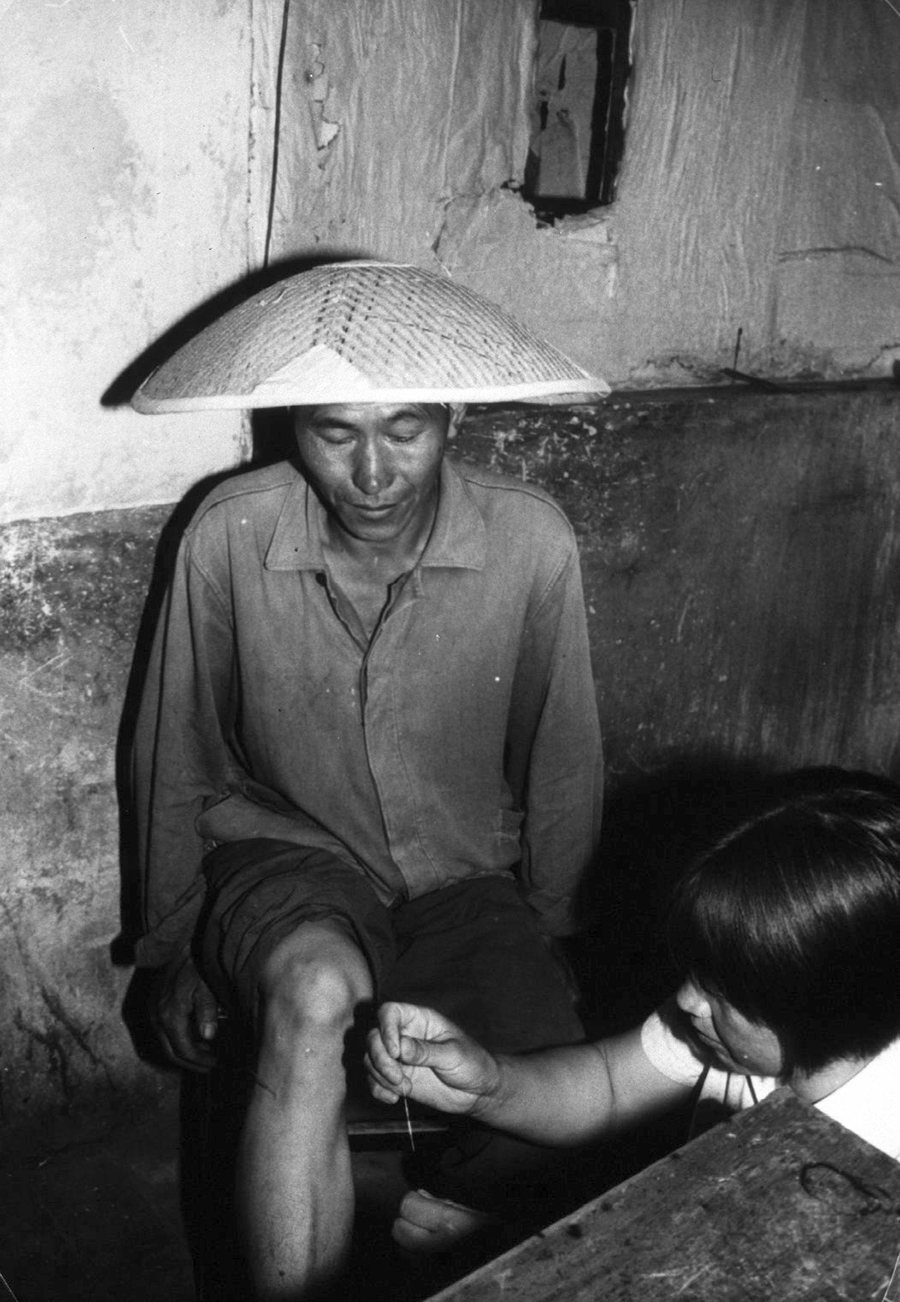

A Chinese barefoot doctor uses her needles to treat a production brigade worker. World Health Organization photo by D. Henrioud. Verso: WHO/18315. WPRO. Acupuncture. China. SM 12.1979.
From the Massive Open Online Course «Examining African Contributions to Global Health»
Linking to photographers, with Creative Commons Licence BY-SA 4.0:

Textbooks, like the Delorean pictured above, can be used as time machines to help us learn about the early attempts to educate and persuade a new generation of psychology students. (CC BY-SA 4.0; Justin Morton & Oto Godfrey)
From the course «History of Psychology»
Linking to a journal:
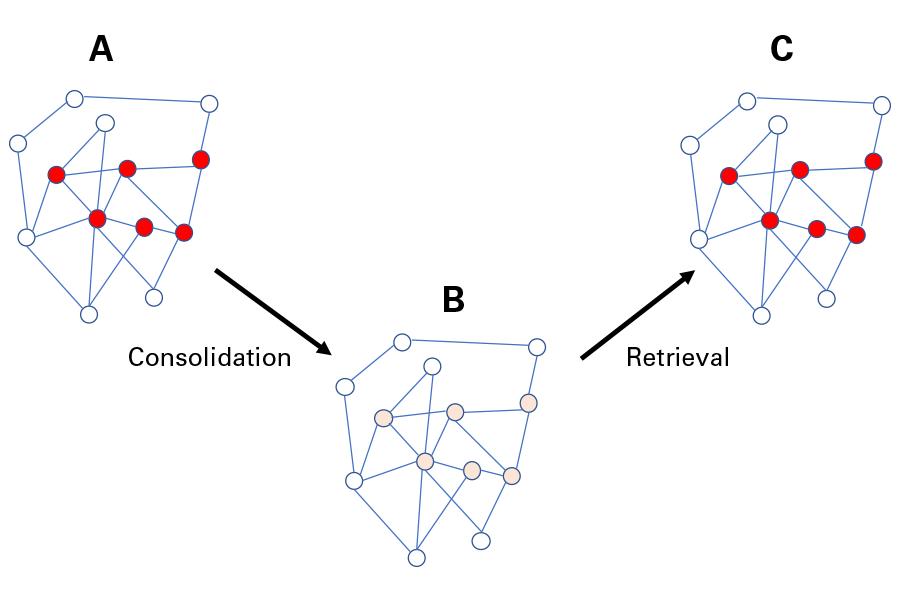
Neural model of memory. During a learning experience, a specific neural circuitry (also called engram) becomes activated and encodes the information (A). The red dots illustrate activated neurons. After memory consolidation, this information is stored in long-term memory in a low-activity state (B). When learned information is retrieved, the same neural circuitry becomes activated (C). Adapted from Josselyn et al., Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Sep;16(9):521-34.
From the course «Learning and Memory»
Public Domain photograph:

Walt Whitman at the age of 36 (© Wikimedia, public domain)
From the Massive Open Online Course «Literature in the Digital Age»
Own work:

Hand zooming in on a tablet screen (© New Media Center, University of Basel)
From the Massive Open Online Course «Literature in the Digital Age»
Linking to a journal, with Creative Commons Licence BY-NC-ND 3.0:
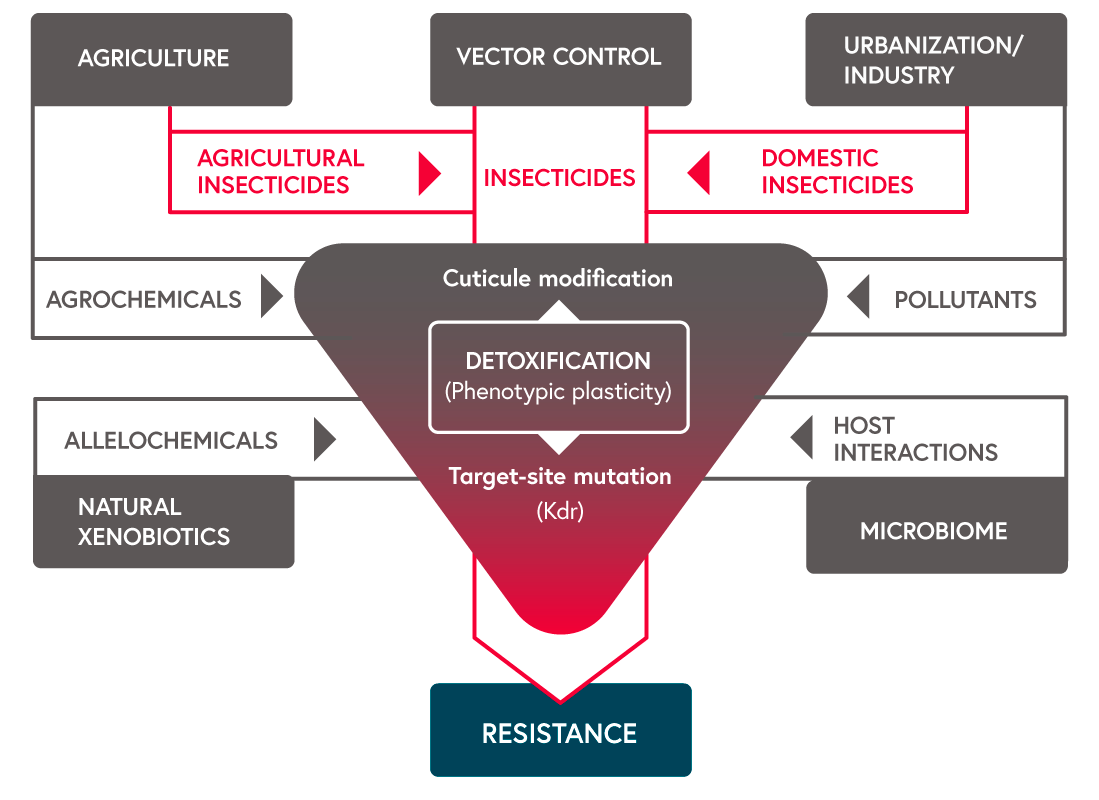
Insecticide-based selection pressures are shown as red arrows. Other factors potentially affecting resistance mechanisms are agrochemicals from agriculture, pollutants from urbanisation or industry, allelochemicals from natural xenobiotics, or host interactions from microbiomes. (Nkya TE et al, 2013. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0; redrawn from original figure)
From the Massive Open Online Course «The Resistant Mosquito»
